Glycan Processing
Low-cost, high performance glycan processing enzymes
Modify and release glycans for downstream applications.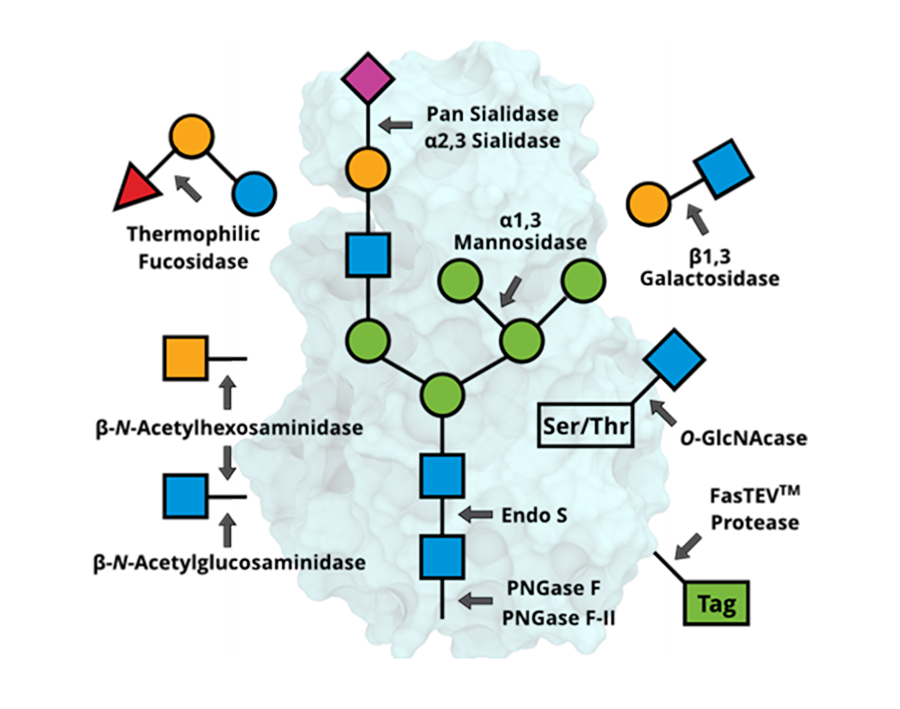
Existing glycan processing enzymes can have drawbacks:
- High cost
- Suboptimal performance
- Lack of detail regarding conditions for efficiency (e.g., required pH, buffers, substrates, and protocols)
- Require harsh conditions that may impact downstream workflows
- Heterogeneity between batches
Your resources are too precious to pay high prices or repeat experiments due to inconsistent results.
GlycAN Processing
Our Glycan Processing Enzymes
Are Reliable And Affordable
Low Prices
Our glycan processing enzymes are more cost-effective than our competitors.
Documentation
Performance data, as well as defined conditions for efficiency, are available in our online store for all enzymes.Consistency
Our enzymes are produced recombinantly and subjected to a rigorous QA process, ensuring consistent results between batches.Scientists deserve tools that advance their work.
We know how frustrating it can be to see your progress limited by cost of materials or uncertainty regarding their performance. Since our inception in 2009, we have developed accessible, effective glycoscience products to democratize the field so that all scientists can push the boundaries of their research and industry applications.




JUST 3 STEPS TO
Confidently Run Downstream Analyses at Lower Costs.
1. Review the documentation
Peruse our suite of glycan processing enzymes for performance data, protocols, and conditions for efficiency.
2. Order an enzyme
Save money on enzymes with excellent performance.
3. Get Results
Run the protocol to cleave the glycan of interest with confidence.Lectenz bio
Glycoscience Made Simple
At Lectenz Bio, we know that you want to use glycoscience data to answer critical questions in your field. To do that, you need to modify and release glycans. The problem is, glycan processing enzymes are costly and can have substantial limitations.
We believe scientists deserve tools that are both robust and affordable, and we understand that lack of access to high performance glycan processing enzymes is a barrier to scientific progress. This is why we developed well-documented, thoroughly tested glycan processing enzymes and priced them competitively.

We make affordable and effective glycan processing enzymes available in just three steps:
- 1. Review the documentation
- 2. Order an enzyme
- 3. Get results
Get started by reviewing and ordering our enzymes. And in the meantime, take a look through a list of publications from research teams that have already used our technologies to improve their glycan detection applications. So you can stop feeling uncertain and instead incorporate glycoscience data into your work with confidence.
Glycan Processing Enzymes
| Product Name | Catalog Number | Amount | Glycoprotein? | pH Range | Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNGase F | GE0101 | 4,000 units; 20,000 units | No | 6.0-9.0 | Cleaves N-linked glycans without core α1,3 fucose |
| PNGase F-II | GE0201 | 100 units | No | 5.5-8.0 | Cleaves N-linked glycans with or without core fucose, both α1,6 and α1,3 |
| α2,3 Sialidase | GE0302 | 5,000 units | No | 4.0-8.0 | Cleaves terminal α2,3-linked sialic acid |
| O-GlcNAcase | GE0401 | 1,000 units | No | 6.0-9.0 | Cleaves O-linked β-N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) |
| FasTEV™ Protease | GE0501 | 1,000 units | No | 6.5-8.0 | Cleaves the peptide bond between a glutamine and a glycine or serine of the consensus sequence ENLYFQ▲G/S |
| Thermophilic Fucosidase | GE0601 | 5,000 units | No | 3.5-8.0 | Cleaves α1,2/3/4/6-linked fucose at high temperature |
| Pan Sialidase | GE0701 | 5,000 units | No | 3.5-7.5 | Cleaves terminal sialic acid |
| Endo S | GE0801 | 2,500 units | No | 5.5-6.5 | Cleaves N-linked glycans from IgG heavy chain |
| β1,3 Galactosidase | GE0901 | 2,000 units | No | 4.5-7.5 | Cleaves terminal β1,3-linked galactose |
| α1,3 Mannosidase | GE1001 | 1,000 units | No | 5-8.5 | Cleaves terminal α1,3-linked mannose |
| β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase | GE1101 | 500 units | No | 3.5-7.5 | Catalyzes the hydrolysis of the non-reducing terminal GlcNAc and GalNAc |
| β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase | GE1201 | 500 units | No | 3.5-7.5 | Catalyzes the hydrolysis of the non-reducing terminal GlcNAc |

Glycoproteins digested with Lectenz Bio PNGase F or PNGase F-II. A. PNGase F is commonly used to cleave N-glycans from mammalian proteins with or without α1,6-core fucosylation, such as bovine ribonuclease B (RNase B). B. PNGase F-II can also cleave RNase B, as well as α1,3-core fucosylated N-glycans from insect or plant proteins, such as horseradish peroxidase (HRP).