Glycan Detection
Glycan Detection Tools For Robust Results
Incorporate glycoscience data into research and industry applications with confidence using novel reagents and user-friendly kits.
Did you know?
Existing glycan detection approaches can have limitations:
- False positives or false negatives due to lack of specificity
- Inconsistent detection of many glycan structures due to poor affinity
- Context-dependent results due to glycan presentation
- Heterogeneity between reagent batches
- Expensive instrumentation
- Reliance on specialized expertise
- Delays receiving results
As a scientist, your work is too important to rely on inconsistent results or inaccessible tools.
Lectenz Bio’s Glycan Detection Reagents Overcome These Challenges
Confidence
Improve your methods with reagents that have the specificity and affinity to accurately detect glycans of interest.
Ease of Use
Our glycan detection kits can easily be integrated into your existing workflow, saving time and money.
Consistency
All our reagents are produced recombinantly, ensuring consistent results between batches.
Scientists deserve tools that advance their work.
We know how frustrating it can be to have uncertainty in your data or see your work stalled due to resource-intensive methodology.
Since our inception in 2009, we have developed accessible, effective glycoscience products to democratize the field so that all scientists can push the boundaries of their research and industry applications.





Get Low-cost, Specific, and Consistent Glycan Detection Results.
1. Order a reagent kit
Purchase a reagent kit that will detect the glycan of interest. To run a control, also order an enzyme to cleave the glycan.
2. Select your protocol
We have protocols available for download depending on the assay you need to run. You can also use your own protocol, or ask support if you’re not sure.
3. Run your experiment
Get clear, prompt results and trust in your data’s integrity, assured by the exceptional specificity, affinity, and consistency of our reagents.
Lectenz bio
Glycoscience Made Simple
At Lectenz Bio, we know that you want to use glycoscience data to answer critical questions in your field. To do that, you need glycan detection tools you can use with confidence. The problem is, many current solutions can be inconsistent, which leads to uncertainty.
We believe scientists deserve tools that are both reliable and affordable, and we understand that lack of effective and accessible glycan detection solutions is a barrier to scientific progress. This is why we created our patented Lectenz® platform, to develop reagents that enable glycan detection without specialized glycoscience expertise.

We make clear, accurate, and timely glycan detection results available in just three steps:
Get started by purchasing your reagent kit. And in the meantime, take a look through a list of publications from research teams that have already used our technology to improve their glycan detection applications. So you can stop feeling uncertain and instead have confidence in your results.
Glycan Detection Protocols
Western Blotting
Download the Western Blotting Protocol PDF
For a basic overview, see the video and protocol below.
Immunoprecipitation
Immunoprecipitation is an affinity purification technique that uses binding agents immobilized to solid matrix, such as agarose or magnetic beads, to purify antigens from solutions. The technique can also be used to purify biological complexes out of solution as long as one member of the complex contains the antigen corresponding to the binding agent. For use with our glycan detection reagents, see the protocol below.

Bovine serum IP using biotinylated SiaFindTM Pan-Specific Lectenz and streptavidin magnetic beads. The sialylated serum globulin, serpin G1, is among the glycoproteins pulled down from serum solution, as seen in the western blot.
Download the Immunoprecipitation Protocol PDF
Immunohistochemistry
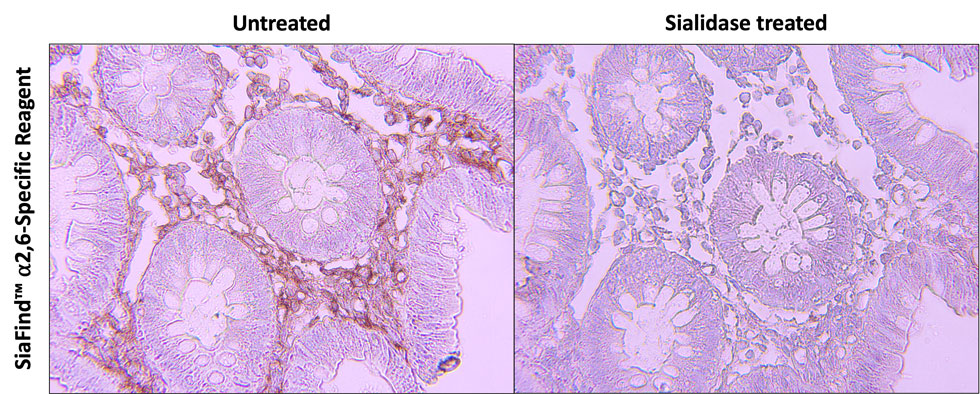
Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence with biotinylated Pan-Specific Lectenz® on human skin cells

Human skin cells stained with SiaFind™ Pan-Specific Lectenz® precomplexed with Streptavidin-Alexa Fluor 488 (green)
Mounted with ProLong Gold Antifade Mountant with DAPI (blue)
Images courtesy of Dr. Hans Wandall and Mikkel Andersen, University of Copenhagen Centre for Glycomics
Protocols: Pan-Specific numbers 10, 17, and 23; α2,3-Specific numbers 8, 9, and 11.
ELISA
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a plate-based technique that uses binding agents, such antibodies or lectins, to detect and quantify antigens in a sample. There are many variations in the design of the assay, such as direct, indirect, and sandwich ELISAs. To perform a basic ELISA with our glycan detection reagents, see the protocol below.

Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry is a technique that uses lasers to measure the fluorescence of single cells or particles in solution.
MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells stained with fluorescent Lectenz®

Cells were labeled by Cureline Molecular Services, LLC.
SiaFind™ Pan-Specific Lectenz® Surelight 488 or SiaFind™ α2,3-Specific Lectenz® Surelight 488 was used to stain MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Overlay of untreated cells (black) and sialidase treated cells (red).
Protocols: Pan-Specific numbers 1 (same as α2,3-Specific number 1), 2, 4, 6 (same as α2,3-Specific number 3), 9, 10, 11, 12, 13 (same as α2,3-Specific number 5), 15, 18, 19, 20 (same as α2,3-Specific number 7), and 22 (same as α2,3-Specific number 13); α2,3-Specific numbers 6, 9, 10, 13, and 14.