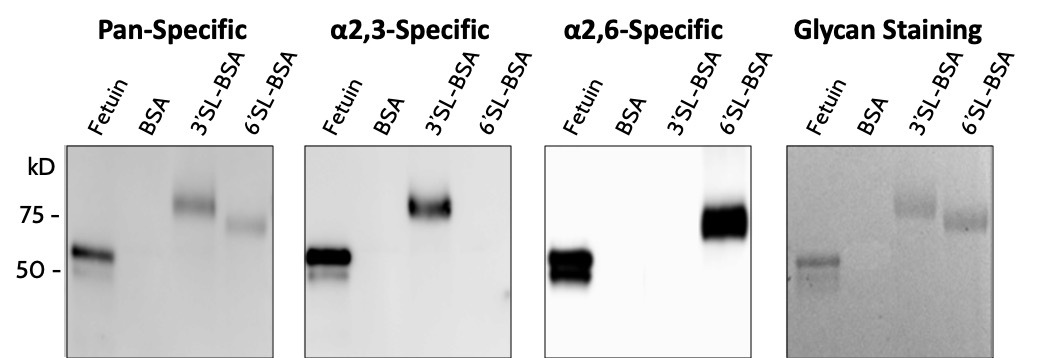
Citations
1. Dabelsteen S, Pallesen EMH, Marinova IN, Nielsen MI, Adamopoulou M, Rømer TB, Levann A, Andersen MM, Ye Z, Thein D, Bennett EP, Büll C, Moons SJ, Boltje T, Clausen H, Vakhrushev SY, Bagdonaite I, Wandall HH. Essential Functions of Glycans in Human Epithelia Dissected by a CRISPR-Cas9-Engineered Human Organotypic Skin Model. Dev Cell. 2020 Sep 14;54(5):669-684.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.06.039. Epub 2020 Jul 24. PMID: 32710848; PMCID: PMC7497784.
2. Büll C, Nason R, Sun L, Van Coillie J, Madriz Sørensen D, Moons SJ, Yang Z, Arbitman S, Fernandes SM, Furukawa S, McBride R, Nycholat CM, Adema GJ, Paulson JC, Schnaar RL, Boltje TJ, Clausen H, Narimatsu Y. Probing the binding specificities of human Siglecs by cell-based glycan arrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Apr 27;118(17):e2026102118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2026102118. PMID: 33893239; PMCID: PMC8092401.
3. Nason R, Büll C, Konstantinidi A, Sun L, Ye Z, Halim A, Du W, Sørensen DM, Durbesson F, Furukawa S, Mandel U, Joshi HJ, Dworkin LA, Hansen L, David L, Iverson TM, Bensing BA, Sullam PM, Varki A, Vries E, de Haan CAM, Vincentelli R, Henrissat B, Vakhrushev SY, Clausen H, Narimatsu Y. Display of the human mucinome with defined O-glycans by gene engineered cells. Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 1;12(1):4070. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24366-4. PMID: 34210959; PMCID: PMC8249670.
4. Canals Hernaez D, Hughes MR, Li Y, Mainero Rocca I, Dean P, Brassard J, Bell EM, Samudio I, Mes-Masson AM, Narimatsu Y, Clausen H, Blixt O, Roskelley CD, McNagny KM. Targeting a Tumor-Specific Epitope on Podocalyxin Increases Survival in Human Tumor Preclinical Models. Front Oncol. 2022 May 4;12:856424. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.856424. PMID: 35600398; PMCID: PMC9115113.
5. Ahmad A, Georgiou PG, Pancaro A, Hasan M, Nelissen I, Gibson MI. Polymer-tethered glycosylated gold nanoparticles recruit sialylated glycoproteins into their protein corona, leading to off-target lectin binding. Nanoscale. 2022 Sep 22;14(36):13261-13273. doi: 10.1039/d2nr01818g. PMID: 36053227; PMCID: PMC9494357.
6. Sørensen DM, Büll C, Madsen TD, Lira-Navarrete E, Clausen TM, Clark AE, Garretson AF, Karlsson R, Pijnenborg JFA, Yin X, Miller RL, Chanda SK, Boltje TJ, Schjoldager KT, Vakhrushev SY, Halim A, Esko JD, Carlin AF, Hurtado-Guerrero R, Weigert R, Clausen H, Narimatsu Y. Identification of global inhibitors of cellular glycosylation. Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 20;14(1):948. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36598-7. PMID: 36804936; PMCID: PMC9941569.
7. Lin CL, Sojitra M, Carpenter EJ, Hayhoe ES, Sarkar S, Volker EA, Wang C, Bui DT, Yang L, Klassen JS, Wu P, Macauley MS, Lowary TL, Derda R. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of genetically-encoded multivalent liquid N-glycan arrays. Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 28;14(1):5237. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40900-y. PMID: 37640713; PMCID: PMC10462762.
8. Mijdam R, Bijnagte-Schoenmaker C, Dyke E, Moons SJ, Boltje TJ, Nadif Kasri N, Lefeber DJ. Sialic acid biosynthesis pathway blockade disturbs neuronal network formation in human iPSC-derived excitatory neurons. J Neurochem. 2023 Aug 31. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15934. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37650222.
9. Orozco-Moreno M, Visser EA, Hodgson K, Hipgrave Ederveen AL, Bastian K, Goode EA, Öztürk Ö, Pijnenborg JFA, Eerden N, Moons SJ, Rossing E, Wang N, Haan N, Büll C, Boltje TJ, Munkley J. Targeting aberrant sialylation and fucosylation in prostate cancer cells using potent metabolic inhibitors. Glycobiology. 2023 Oct 17:cwad085. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwad085. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 37847613.
10. Boelaars K, Goossens-Kruijssen L, Wang D, de Winde CM, Rodriguez E, Lindijer D, Springer B, van der Haar Àvila I, de Haas A, Wehry L, Boon L, Mebius RE, van Montfoort N, Wuhrer M, den Haan JMM, van Vliet SJ, van Kooyk Y. Unraveling the impact of sialic acids on the immune landscape and immunotherapy efficacy in pancreatic cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Nov;11(11):e007805. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-007805. PMID: 37940346; PMCID: PMC10632901.
11. Monti M, Milanetti E, Frans MT, Miotto M, Di Rienzo L, Baranov MV, Gosti G, Somavarapu AK, Nagaraj M, Golbek TW, Rossing E, Moons SJ, Boltje TJ, van den Bogaart G, Weidner T, Otzen DE, Tartaglia GG, Ruocco G, Roeters SJ. Two Receptor Binding Strategy of SARS-CoV-2 Is Mediated by Both the N-Terminal and Receptor-Binding Spike Domain. J Phys Chem B. 2024 Jan 18;128(2):451-464. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.3c06258. Epub 2024 Jan 8. PMID: 38190651; PMCID: PMC10801686.
12. Huang L, Kondo Y, Cao L, Han J, Li T, Zuo B, Yang F, Li Y, Ma Z, Bai X, Jiang M, Ruan C, Xia L. Novel GNE missense variants impair de novo sialylation and cause defective angiogenesis in the developing brain in mice. Blood Adv. 2024 Feb 27;8(4):991-1001. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023011490. PMID: 38237079; PMCID: PMC10879683.
13. Boelaars K, Rodriguez E, Huinen ZR, Liu C, Wang D, Springer BO, Olesek K, Goossens-Kruijssen L, van Ee T, Lindijer D, Tak W, de Haas A, Wehry L, Nugteren-Boogaard JP, Mikula A, de Winde CM, Mebius RE, Tuveson DA, Giovannetti E, Bijlsma MF, Wuhrer M, van Vliet SJ, van Kooyk Y. Pancreatic cancer-associated fibroblasts modulate macrophage differentiation via sialic acid-Siglec interactions. Commun Biol. 2024 Apr 9;7(1):430. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06087-8. PMID: 38594506; PMCID: PMC11003967.